Prof. Lee Sung-wook and Team Develop Inhibiting Substance for Liver Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer

Found ways to effectively track and control the metastasis of colorectal cancer.
Effects proven through animal testing, results published in the prestigious journal in human digestive system, Gastroenterology.
Professor Lee Sung-wook (Department of Molecular Biology) and his research team developed a new substance which could effectively track and control the metastasis of cancer cells to the liver, which is one of the major reasons for death among colorectal patients.
“Nucleic Acid Aptamer” developed by Lee’s team is a substance that can prove the principle in which carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) that sparks the metastasis to the liver is revealed and effectively controlled. Professor Lee proved though animal testing that Nucleic Acid Aptamer is combined with certain parts of the CEA and prevents the metastasis of cancer cells to the liver.
The research results were published in the July edition (July 1) of Gastroenterology, which is the most prestigious journal for digestive system studies. Also, its importance has been recognized and selected as the most noteworthy research which was individually introduced on the website. In addition, Korea’s major Bio Science website, BRIC, introduced the research results in the “Proud Korean” section which highlights Korean scientists’ publications in prestigious international journals.
Colorectal cancer is one of the world's most prevalent cancers, and Korea ranks 4th globally in colorectal cancer incidents. Colorectal cancer can be confirmed with high CEA level, which is the cancer marker. If there are excessive CEA, then it is common to experience accelerated metastasis of cancer cells to the liver. A major cause of death for colorectal cancer patients is metastasis to the liver, which occurs in 2 to 7 out of 10 people. The probability of relapse is high, and prognosis is not good.
Professor Lee is the first to develop a Nucleic Acid Aptamer that combines with certain parts of CEA that are major factors in liver metastasis, and by regulating this, Lee’s team found ways to effectively control spreading to liver. This substance not only prevents the colorectal cancer cells from spreading to liver but also tracks the liver metastasis of cancer cells by leading to extinction of the cells, opening a new way to diagnose and also cure the disease.
Nucleic Acid Aptamer is a biopolymer substance made of Nucleic Acid and has similar characteristics with antibodies, so it can easily combine with target cells. Since it can easily synthesize and transform like low molecular weight chemicals, mass production is possible according to purpose. With high transmittance to the cancer cell tissue and low incidences of infection or low level of toxins, it is gaining attention as a next-generation new drug substance.
“The research results proved that CEA is the major factor accelerating the spread of cancer cells to the liver,” said Professor Lee. “With development of the Nucleic Acid Aptamer, we were able to present the transformation process and environment in which cancer cells spread to the liver. This will eventually lower the death rate due to colorectal cancer.”
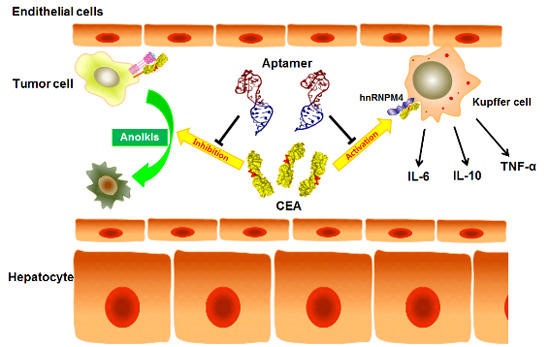
Ways to control spreading of colorectal cancer by Nucleic Acid Aptamer targeting CEA
Nucleic Acid Aptamer is combined to the “PELPK” of the CEA that spreads cancer cells to the liver and undermines the initial stage of metastasis by CEA, fundamentally preventing the spread of cancer.